WAN and LAN
A wide area network is a telecommunications network that extends over a large geographic area for the primary purpose of computer networking. Wide area networks are often established with leased telecommunication circuits.
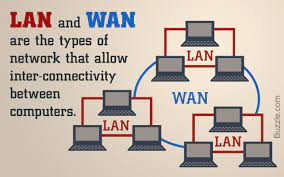
LAN
LAN stands for Local Area Network. As its name implies, a LAN is a network limited to a small area, like a home or office, and is usually confined to a single building. The LAN can consist of computers, smartphones, TVs and tablets. A wireless LAN is usually limited to the radius of a wireless access point which can be a couple of hundred feet. However, this distance can be extended by linking additional wireless access points to the network. A Wi-Fi router is an example of a wireless access point.
A LAN connection is a high-speed connection to a LAN. On the IUB campus, most connections are either Ethernet (10 Mbps) or Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps), and a few locations have Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) connections.
WAN
WAN stands for Wide Area Network. A WAN is a network covering any large geographic area. WANs can be as large as a state, a country, or the world. The Internet itself is a type of WAN, because it covers the entire globe. Although a network connecting LANs in the same city, like a group of offices belonging to the same company, these are usually called metropolitan area networks.
A WAN connects several LANs, and may be limited to an enterprise (a corporation or an organization) or accessible to the public. The technology is high speed and relatively expensive. The Internet is an example of a worldwide public WAN.